 |
|
We feel immensely pleased to bring out this website on Acupressure for the readers who sincerely want to know about it. We hope our website will be useful for those enthusiasts who wish to practice Acupressure to provide relief to the human being suffering from various ailments.
It is an effort to put forth the basics of the science of acupressure and to clarify the possible doubts which may occur while practising it. Techniques discussed in this website, if used in a proper manner will not only bring desired results but also reduce the excessive intake of medicines on the part of the patient.
Whatever we studied and experienced during our professional career, we have tried to put it in front of you in simple language. We have taken special pains to simplify the difficult medical terms so that one can understand them easily.
It took us very long to plan and create this website on Acupressure. We are not professional writers, but the intense desire to share our knowledge with you and a wholehearted effort to make you acquainted with this miraculous science, have resulted in this practical website, about Acupressure.

Acupressure is an ancient mode of treatment, known to mankind for last 6000 years. Till date thousands of people from various countries have learned this mode of treatment and many people are practising it. It is now a widely accepted mode of treatment all over the world.
Acupressure is a very natural way of treatment.it is as natural as one's instinct to hold his head while having a headache or rubbing against a painful part.
In our day to day practice too, knowingly or unknowingly we have adapted acupressure therapy.
It can be very well explained through the following examples:
1) Tying a thread around the waist, wrist & ankle of a baby.
2) Wearing a locket
3) Indian females wear a vermillion (bindi) on a point which is very important from acupressure point of view.
4) Similarly different ornaments worn especially by Indian females like bangles, anklets, etc. are beneficial as they stimulate the acupressure points.
Acupressure is a scientific mode of treatment based on the principle of pressure & stimulation. It flushes out the toxins from affected part & relaxes it by stimulating the related points through acupressure.
If we split the word “acu pressure”, we will easily understand its basic principal.
Viz. Acu = To remove
Pressure = applying that much force, para enough to cure the disease.
Thus acupressure is to remove a disease by applying pressure. Such pressure is applied either manually (by fingers, thumbs, knuckls) or through various acupressure instruments.
Every person has the resistance power against the disease. But in some individual it becomes weak or goes dormant due to certain adverse conditions. Acupressure awakens this dormant power and energizes it.
There are some other therapies which work on the similar basis of applying pressure and removing disease. These are practiced and recognized in various parts of the world.
These therapies are: -
• SHAITSU
• ZONE THERAPY
• MERIDIANS
• REFLEXOLOGY
Here we are going to study the phenomenon that occurs in our body after applying the pressure. Before coming to this point, let us see” how do we get ill?”
This can be explained by the following example:-
If we fill a bottle with clean water and keep it for some days, we will observe that there is a layer of sedimented particles at the base of the bottle, due to the effect of atmosphere.
Similarly, in a diseased body, toxins in the form of “Crystals” get settled down at various sites especially at fingertips and toe tips where nerve ending is present. This causes disturbance in the blood flow and the person becomes sick.
Acupressure breaks these crystals to establish normal blood flow and regain health. This is done through the stimulation of various acupressure points.
Acupressure points are the places on the skin which are sensitive to the bio energy flowing in our body. Traditionally speaking, these points are junctions of special pathways which carry bio-energy/ bio-electricity. Stimulation of these points through acupressure triggers the release of endorphins. Endorphins are the neurochemicals that relieve pain. As a result; pain is relieved and the blood circulation and oxygen flow is increased. The affected part is thus relaxed as healing takes place.
By normalizing the blood circulation and increasing the flow of oxygen, acupressure increases the body's resistance against various diseases and mental stress.
In acupressure, local symptoms are considered as an expression of the condition of a body as a whole. E.g. (i) a tension headache may be rooted in the shoulders or neck congestion.
(ii) Difficulty in breathing may be related to mental stress.
Thus when we apply acupressure to relieve pain and discomfort, it also cures the basic reason behind it. In this way the imbalance of energy is corrected before it is developed into a disease.
Like any other science; acupressure is based on certain principles which can be described as follows:-
1) Treatment is done after considering both mental & physical aspects of the disease. e.g. by stimulating brain points, the patient is brought into the positive frame of mind. Treatment is concluded by treating kidney points which flushes out the blockage through urination.
2) Acupressure points are present in various reflex areas. The reflex areas have nerve endings (in hand & feet) & are connected to various organs in the manner as a switch is connected to a tubelight. That's why when we stimulate a point through acupressure, the connected organ is also stimulated.
3) The blockage created by toxins in our body hampers the normal body functioning. As a result, the person gets ill. Acupressure removes such blockage to establish normal body functions.
4) The saturation of harmful substances causes crystallization under the skin of fingertips and toes. Acupressure breaks these crystals and helps to flush it out through urination.
5) Acupressure maintains the balance between Yin and Yang i.e. bioenergy of our body. In diseased conditions, there is a leakage of energy which is repaired by acupressure.
1) Acupressure is easy to practice.
2) Acupressure is the safest mode of practice without any side effects.
3) Acupressure revitalizes body's immune system by increasing resistance.
4) Acupressure normalizes the functioning of the endocrine system.
5) Musculature becomes more flexible.
6) Disorders related to nervous systems are cured.
7) Acupressure maintains the circulation and supply of various nutrients in the body.
8) Acupressure improves the skin texture and enhances its glow; it also reduces wrinkles.
9) Acupressure gives soothing effect in mental disorders.
10) No special instruments are required for acupressure. Acupressure can be done manually.
A person doing acupressure should keep in mind the following things:-
1) Start the treatment with the brain points.
2) Start the treatment from the left side of the body. As the heart lies in the left, circulation is more powerful.
3) There should be a gap of at least 1 hour between the meals & the treatment.
4)If the patient is taking any medicine, acupressure should be done ½ an hour after taking the medicine.
5) There should be a gap of ½ an hour if the patient has just taken a bath.
6) Maximum 2 sittings a day can be done.
7) Patients who have faith in acupressure give better results as they don't have any suspicion in mind. So the therapist should assure the patient of betterment before starting the treatment.
8) Therapist should treat the patient with sincerity, devotion and a gentle, soothing attitude.
9) Counselling is necessary if the patient is depressed or sad. Start the treatment after bringing the patient in a positive frame of mind.
10) Only that much pressure which is tolerable by the patient should be applied.
11) Pressure should range from feather touch to body weight pressure; as per the requirement.
12) Time: duration of applying pressure depends on the severity of the disease and age of the patient. It ranges from minimum of 20 seconds and maximum up to 90 seconds.
13) On delicate areas like face and abdomen, pressure should be applied only for 3 seconds.
14) Position of the patient: make the patient sit or lie down as per the requirement.
15) Remove your finger with jerk after applying pressure.
16) Therapist's hands should be clean with nails properly and evenly cut.
17) Don't treat the patient if you yourself (therapist) are not well.
18) The place of treatment should be clean, quiet and isolated.
19) In case of a fracture, exclude that area. If possible, avoid the treatment till the patient gets well.
20) Don't apply pressure on scars.
21) Don't give treatment during pregnancy.
22) If the patient is under the influence of stimulants or alcohol, avoid treating him/her.
23) Don't treat the patient when he is hungry.
24) Jimmy should be used only on palms and soles, not on bony areas.
25) Kidney points should be taken at the end of the treatment.
1) Position of the patient: patient should sit or lie down without crossing limbs.
2) Avoid eating spices of all types.
3) Avoid sour things like pickle, curd and vinegar
4) Avoid ice-cream, cold drinks or food with preservatives.
5) Avoid non-vegetarian diet, sea food etc.
6) Avoid mental stress. Think positive and cooperate with the therapist during the treatment.
There are different methods of applying pressure which are as follows :-
Manual Methods :
1. single finger
2. double finger
3. thumb
4. both the thumbs
5. flat palm
6. both the palms
7. elbow on more fleshy areas like hips and buttocks
Instruments Used :
1. jimmy
2. energy roller
3. vibrator
4. spine roller
5. other measures like electrical vibrator for cervical regions , etc.
Types of Pressure :
while treating the patient, pressure can be applies in following ways, as per requirement :-
1. steady
2. steady & deep
3. rotating : clockwise ( sedative effect)
Anticlockwise (stimulating effect)
4. rubbing : rub up and down
5. sliding : slide the palm from above downwards, remove. pressure, repeat.
6. push & pull : apply and release pressure alternatively.
7. clutching : by grasping and ungrasping the affected part.
8. vibrating : by using an electrical vibrator.
1. no side effects.
2. non violent, non surgical process.
3. no need to administer any medicine.
4. painless mode of treatment.
5. easy and uncomplicated.
6. economical.
7. self treatment is possible.
8. doesn't clash with any other mode of treatment.
1. mental satisfaction of curing a patient.
2. good source of income.
3. as the success rate increases, the therapist gains respect, good reputation and a better social position.
Since we are now well equipped with all the necessary information regarding acupressure, let's study it in detail now.
As we have discussed earlier; Acupressure consists of :-
1. SHIATSU
2. ZONE THERAPY
3. MERIDIANS
4. REFLEXOLOGY
We are going to study reflexology and meridians with special emphasis on meridians about which we are going to discuss thoroughly.
So in this 'magic touch therapy'. lets study reflexology first.
Reflexology is a science based on the principal that there are reflex areas in feet and hands which are connected to all systems of the body.
It provides knowledge about the reflex areas and points, and their connection with different parts of the body.
The basic concept of reflexology is that the whole human body is interconnected and that imbalance in one part of the body is reflected in changes elswhere in the body.
Many important acupressure points lie in the reflex areas of hands and feet. there is thus a cord relationship between reflexology and acupressure. Reflexology is rather part of acupressure.
1. Reduces stress.
2. improves circulation
3. cleans the body of impurities and toxins.
4. revitalizes energy levels.
5. it also has diagnostic value to some extent as it helps to locate the problem area.
6. gentle, generalized foot massage done at home is relaxing to some extent.
7. relieves pain and helps to restore body's natural balance and well being.
Reflexology comprises of following parts:-
A. Foot Reflexology
B. Hand Reflexology
C. Reflexology of vertebral column
Reflex points on the sole of the foot are studied under foot reflexology.

Working of foot Reflexology
Foot acupressure works by influencing the flow of vital life force throughout the system. a complete healing network of energy carrying channels is said to terminate in the feet. at the end of each channel, is an organ, a gland or other body parts. there is an acupresuure point at the end of each channel. life force (bio energy) moves along these channels like electricity to and from various terminals.
When the life force (bio energy) flows too quickly or too slowly along these channels, the organ malfunctions, producing a disease. when a related acupressure point is treated and stimulated, it helps to restore a normal and balanced flow of energy.
Location of Reflex points :
The reflex points in foot can be better explained through a diagram. there are however certain points which can be located in the right foot. these are :-
1. liver
2. gall bladder
3. appendix
4. ileocaccal valve
similarly some points are located only on the left foot. these are :-
1. heart
2. spleen
3. sigmoid colon.
rest of the points are located on both feet and hands ans are common.
Foot Reflexology is more effective than hand reflexology except in few cases like sprains and pains in players, atheletes, etc.
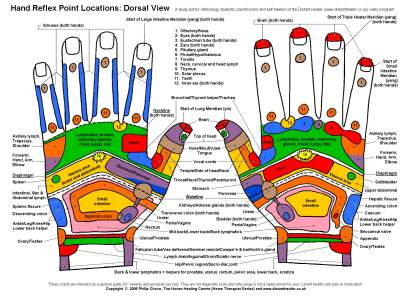
Reflex points situated on the palm of the hand are studied under hand reflexology.
In hand however the reflex points are more congested and a little difficult to locate due to small size of the palm compared to the feet.
Moreover, hand reflexology is not as benificial and effective as foot reflexology. that's why the latter is more popular and is practiced more by most therapists.
All other points and their location is common in both hands and feet, except the following points. they are measured in the same way as the points in foot reflexology.
Left Hand :-
- Heart
- Spleen
- Sigmoid colon
Right Hand :-
- Liver
- Gall bladder
- Appendix
- Ileocaecal valve
The location of hand reflex points is best explained in the above diagram.

Before studying the reflex points on vertebral column, let's get acquainted with our vertebral column, commonly known as back bone.
It is the supporting column of the body located at the center of the back. it supports the body weight and transmits it to the ground through lower limbs.
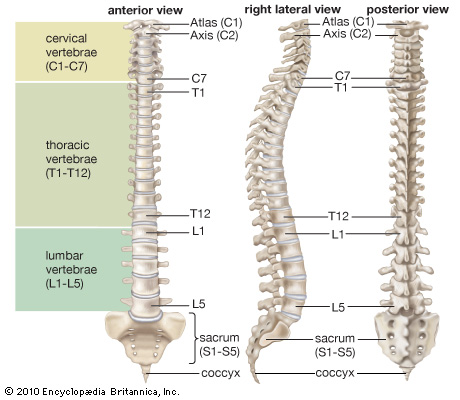
Vertebral column is made up of 33 vertebrae which consists of :-
Cervical vertebrae - 7
Thoracic vertebrae - 12
Lumbar vertebrae - 5
Sacral vertebrae - 5
Coccygeal vertebrae - 4

Among these, cervical, thoracic & lumbar vertebrae are called movable or true vertebrae.
Sacral and coccygeal vertebrae are fixed or false vertebrae.
All vertebrae are joined together with inter vertebral discs.
All thoracic vertebrae support the 12 ribs.
Distribution of nerves in the vertebral column
In the thoracic lumbar and sacral region, the number of vertebrae correspond to the number of spinal nerves, each nerve lying below the corresponding vertebra. thus these are 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar & 5 sacral nerves.
In the cervical region (neck region). there are 8 nerves, 7 in each vertebrae and the 8th lying below the 7th vertebra.
In the coccygeal region, there is only 1 coccygeal nerve.
Length of the vertebral column
It is about 28 inches long in males and 24 inches long in females. the inter vertebral disc contributes to 1/5th of the length of the vertebral column.
Reflex points on the vertebral column
Now we will discuss the reflex points on the vertebral column according to the types of vertebrae through various diagrams.
1. Reflex points on cervical vertebrae.
2. Reflex points on thoracic vertebrae.
3. Reflex points on lumbar vertebrae
4. Reflex points on sacral & coccygeal vertebrae.
The diseases related to each vertebrae is given in the following chart :
Note : Every part of body is controlled by nerves and every one on use nerves connects directly or indirectly with the spine.
Column :
A: Names of vertebrae and nerves in the spine.
B: The areas receiving nerve fibers from these nerves.
C : Some of the conditions that can follow a pressure on or interference with nerves.
| A | B | C |
| C-1 | Blood supply in head, pituitary gland, scalp, bones of face, brain, inner & middle ear, sympathetic nerves system | Headache, nervousness, insomnia, head colds, high blood pressure, migraine, mental conditions, amnesia, epilepsy, infantile paralysis, chronic tiredness, vertigo. |
| C-2 | Eyes, optic nerve, auditory nerve, sinuses, mastoid bones, tongue, forehead. | Sinus troubles, allergies, crossed squint, deafness, erysipelas, eye troubles, earache, fainting, certain cases of blindness. |
| C-3 | Cheeks, outer ear, face bones, teeth, facial nerve. | Neuralgic, neuritis, acme or pimples, eczema. |
| C-4 | Nose, lips, mouth, eustachian tube. | Hay fever, rose fever, catarrh, hard of hearing, adenoids. |
| C-5 | Vocal cords, neck, glands, pharynx. | Laryngitis, hoarseness, throat conditions like sore throat, quinsy etc. |
| C-6 | Neck muscles, shoulders, tonsils. | Stiff neck, pain in upper arms, tonsilities, whooping cough, croup. |
| C-7 | Thyroid gland, bursa in shoulder, elbows. | Bursities, colds, thyroid conditions, goiter. |
| T-1 | Arms from the elbows down including hand wrists & fingers. esophagus, trachea. | Asthma, cough, difficult breathing, shortness of breath, pain in lower arm and hands. |
| T-2 | Heart including valves and covering, coronary arteries. | Functional heart conditions, certain chest pains. |
| T3 | Lungs, bronchial tube, pleura, chest, breast, nipples. | Bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia, congestion, influenza, grippe. |
| T-4 | Gall bladder , common bile duct. | Gall bladder conditions, Juandice, herpes zoster. |
| T-5 | Liver, solar plexus, blood. | Liver conditions, fevers, low blood pressure, anaemia, poor circulation, arthritis. |
| T-7 | Pancreas, islets of langerhans, duodenum. | Diabetes, ulcers gastritis. |
| T-8 | Spleen, diaphragm | Leukemia, hiccoughs |
| T-9 | Adrenals or suprarenals | Allergies, hives. |
| T-10 | Kidenys | kidney troubles, hardening of arteries, chronic tiredness, nephritis, pyelitis. |
| T-11 | Kidneys, ureters. | Skin conditions, like acne, or pimples, eczema, boils etc., autointoxication. |
| T-12 | Small intestine fallopian tubes, lymph circulation. | Rheumatism, gas pains, certain types of sterility. |
| L-1 | Large intestine or colon, inguinal rings. | Constipation, colitis, dysentery, diarrhea, ruptures of hernias. |
| L-2 | Appendix, abdomen, upper leg, caceum. | Appendicitis, cramps, difficult breathing, acidosis, varicose veins |
| L-3 | Sex organs, ovaries, testicles, uterus, bladder, knee. | Bladder troubles, menstrual troubles, like painful or irregular periods, miscarriages, bed wetting, impotency, change of life symptomes, knee pain. |
| L-4 | Prostate gland, muscles of lower back, sciatic nerve. | Sciatica, lumbago, urine trouble, back-ache. |
| L-5 | Lower legs, ankle, feet, toes, arch of the foot. | poor circulation in legs, swollen ankles, week ankles and arches, cold feet, weakness in legs, leg cramps. |
| Sacrum | Hip bones, buttocks | Sacro-iliac conditions, spinal curvatures. |
| Coccyx | Rectum, anus. | Hemorrhoids, piles, pruritus or itching, pain at the end of spine or sitting. |
Some important and ultra effective reflex points in various ailments :-
In case of pain in lower limbs, reflex areas in various parts of the legs are treated :-
(A) On the anterior (front side) of the lower limbs there are 6 points. 3 points on the upper border of the patella (knee cap).
(B) On the posterior part (back) of the lower limbs: along the length from the back og thigh to ankle, there are 21 points, which are divided as follows :-
1. On the back of the thigh 10 points.
2. Along the posterior crease of the knee 3 points.
3. Along the calves 8 points.
These points are located at the midline of the lower limbs (Lengthwise).
There are 8 reflex points on the abdomen. these points are very effective in digestive disorders of all sorts like flatulence; distention, colic, indigestion etc. Location of points is better described by a diagram.
Method of pressure : pressure is applied with both hands. hand is kept flat and pressure is applied using palm and all fingers except the thumb, for 3 seconds in push and pull method. it is commonly called as 3 pp pressure.
Things to be remembered while stimulating the points:-
1. Generally in most of the areas pressure is applied with the fingertips of first or middle finger or a thumb. while applying the pressure, the fingertip should not just rub or massage the surface of the skin but the skin over the point should also move.
2. Sometimes pressure applied with fingertips is not sufficient. in such cases; use knuckles, thumbs or instruments like blunt end of the pen. even elbow can also be used in more fleshy areas like buttocks, hips etc.
3. Pressure should be just enough to stimulate the point. it should be bearable by the patient. a correctly stimulated point remains sensitive for a few minutes.
4. Bruising occurs if too much pressure is applied. it also causes over stimulation of the point.
5. 10-15 further sittings should be given after the patient gets relief, to assure complete cure.
6. Don't touch the treated area immediately after stimulation as it might hinder the process of reestablishment of bio-energy.
Correct methods of stimulating a point are shown in the diagram.
In reflexology, foot reflexology is mainly practiced by majority of the acupressure therapists and it brings brilliant results.
1. When there is some disease in the body, the point on the meridian to which that particular disease is related, becomes very painful, tender & oversensitive.
2. An area surrounding such point is much less painful.
3. The skin over a painful point is different in color than the normal skin. it may be yellowish, whitish or reddish.
4. The skin also might be inflamed & rough. there might be a small pustule over that area.
5. Temperature of the affected area is slightly more than the normal body temperature.
6. If the point is not very painful, the problem is considered to be a minor one. in such cases; steady & slightly hard pressure is applied for a longer time.
7. Some special electrical instruments can also be used to locate the exact position of the point.
8. An acupressure point which is not painful and is not sensitive to a stimuli does not give satisfactory results even if it treated hence attention should be focused only on sensitive and painful points.

What are meridians?
Definition :- Meridians are the vertical, imaginary lines drawn on the body surface, joining acupressure points having therapeutic properties.
There are 14 main meridians (channels) of which 12 are paired and 2 are unpaired. Bioelectricity/energy flows in these channels in a systematic cyclic sequence.
Origin of Meridians
In the pre historic times, Chinese soldiers returning from the war with bullet wounds used to get relif from certain physical ailments they were suffering prior to that wound.
The chinese doctors treating those soldiers found it interesting. they tried to establish a connection between the spontaneous healing and the wounds. by constant research and monitoring they found that there were certainly some factors which promoted healing after the bullet wounds.
After further studies in succeeding years; the researchers discovered that there were certain points in the body which if massaged, heated or punctured; relieve pain and are effective in certain disorders. numerous such points, all over the body were discovered. these points were then systematically arranged according to their pathway along a particular organ to which they were connected. these channels are named after the organ along which it runs.
There are 12 regular meridians called 12 paired meridians and 8 meridians called extraordinary meridians.
Each of the 12 paired meridians relates to one of the 12 internal organs, out of it,
6 meridians are YIN &
6 meridians are YANG.
Of the 8 extra ordinary meridians ;
two runs on the midline.
one at the front called CV/REN meridian.
one at the back called GV/DU meridian.
These 14 meridians have their own independent pathways and acupressure points. other 6 extra ordinary meridians do not have seperate pathway and are not connected to any particular organ.
Thus there are total 14 meridians (12 paired, 1 DU & 1 REN ) which are mainly used for the purpose of the treatment.
The network of meridians connects the internal organs and the outer body of a man with the universe. that's why a person when exposed to certain external factors like cold, heat, dampness etc. becomes ill.
Out of the 12 paired channels: there are 6 channels in the upper limb and 6 in the lower limb.
Meridians of upper limbs :
There are 6 meridians in the upper limbs. among these, 6 are YIN and 6 are YANG meridians.
YIN channels are the meridians which run on the front side (anterior side) of the arm traveling from heart to fingers (above downwards).
YANG channels are the meridians which run on back side (posterior side ) of the arm travelling from fingers to heart(below upwards).
Meridians of lower limbs :
Like the upper limb: there are 6 meridians in the lower limbs too. 3 are YIN and 6 are YANG meridians.
YIN meridians run on the inner side (medial side) of the leg travelling from toes to head (below upwards).
YANG meridians run on the other side (lateral side) of the leg travelling from head to toes (above downwards).
In Acupressure, there are special points which control certain painful conditions like joint pain in different body parts; or certain physiological conditions such as hunger, sleep etc.
A table showing such conditions and their related points is given in following table :-
| 1) | Yawing | L5 |
| 2) | Sleep | LIV 1 |
| 3) | Hunger | LIV 13 |
| 4) | Asthma | CV 22 |
| 5) | Fever | Li 11 |
| 6) | Smoking | Li 19 |
| 7) | Fear | UB 11, H7 |
| 8) | Temper | H 7, GB 41 |
| 9) | upper body pain | Li 4 |
| 10) | lower body pain | St 44, Sp 6, UB 67, St 36, GB 38 |
| 11) | ejaculation | Liv 8, Liv 14, St 29, St 31, Li 18, GB 21, UB 27 |
| 12) | Wet dreams (nocturnal emission) | UB 27 |
| 13) | milk secretion | GB 41 |
| 1) | General bodyache | L 7, UB 60, GB 38 |
| 2) | upper body | Li 4 |
| 3) | lower body | Sp 6, St 36 |
| 4) | upper back | Li 4, GV 13 |
| 5) | middle back | TW 3 |
| 6) | lower back | UB 40, Sp 4, Sp 5, Sp 6 |
| 7) | lower back + abdomen | CV channel all points St 25, Sp 15 (3 pp pressure) |
| 8) | chest & ribs | TW 5, TW 6, P 7 |
| 9) | Arms & shoulders | P 6, GV 13, TW 6 |
| 10) | hands | H 5 |
| 11) | menstrual pain | Sp 6, Sp 10 |
| 12) | neck | GV 13 |
| 13) | ear | P5, P6 |
| 14) | inner thigh | UB 39, UB 40 |
| 15) | testicles | Sp 4, Sp 5, Sp 6 |
| 16) | Penis | Liv 1 |